The advancement of technology has led to significant innovations in sustainable building materials. Modern materials are not only reducing environmental impact but also enhancing energy efficiency, durability, and self-sufficiency in buildings. The integration of smart materials, energy-generating surfaces, and advanced insulation techniques is shaping the future of construction. The following discussion highlights some of the most promising innovations in sustainable building materials and how they are contributing to a greener and more efficient built environment.
Smart Materials and Self-Healing Concrete
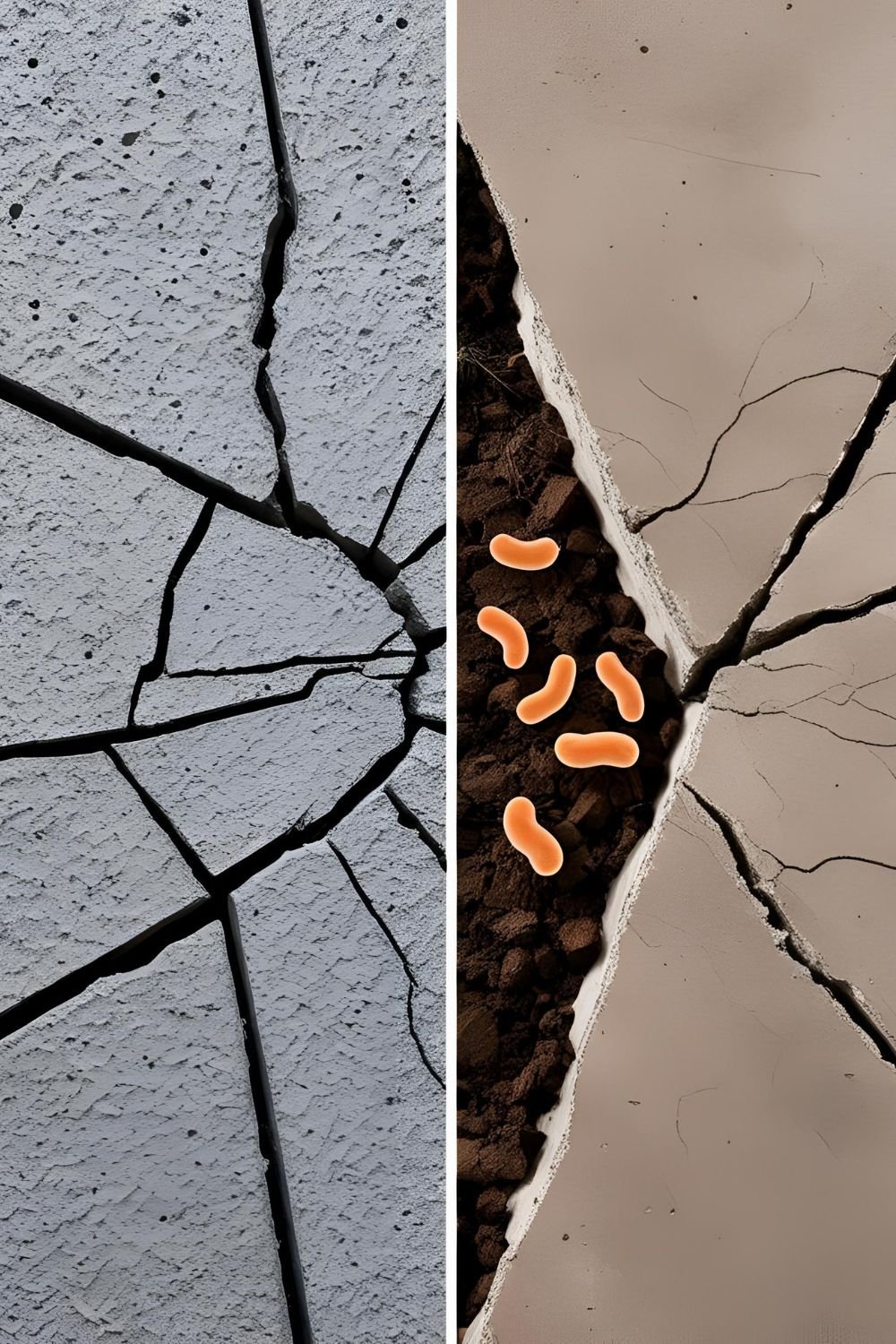
The construction industry has always faced challenges related to material degradation, especially in concrete structures. Cracking in concrete is inevitable over time due to external stress, temperature variations, and structural load. However, self-healing concrete is an innovative material that addresses this issue by autonomously repairing cracks, ensuring long-term durability and minimizing maintenance costs.
Self-healing concrete integrates bacteria-based capsules or microcapsules filled with healing agents like calcium carbonate. When cracks appear and water enters, the bacteria activate, producing limestone that fills the cracks. This process not only extends the lifespan of structures but also reduces the carbon footprint by decreasing the need for frequent repairs and new material production. Another approach is the use of shape-memory polymers that react to environmental stimuli such as heat or moisture, closing cracks naturally.

Besides durability, smart materials like thermochromic and photochromic coatings are also being applied in construction. These materials respond to temperature and light changes, optimizing indoor climate conditions and reducing the dependency on HVAC systems, ultimately leading to energy savings.
Energy-Generating Materials: The Potential of Photovoltaic Glass
The integration of energy-generating materials into buildings is redefining the concept of sustainability. Photovoltaic (PV) glass is a groundbreaking innovation that allows buildings to generate their own electricity while maintaining aesthetics and functionality. Unlike traditional solar panels, PV glass can be used in windows, facades, and skylights, making it a seamless part of architectural design.
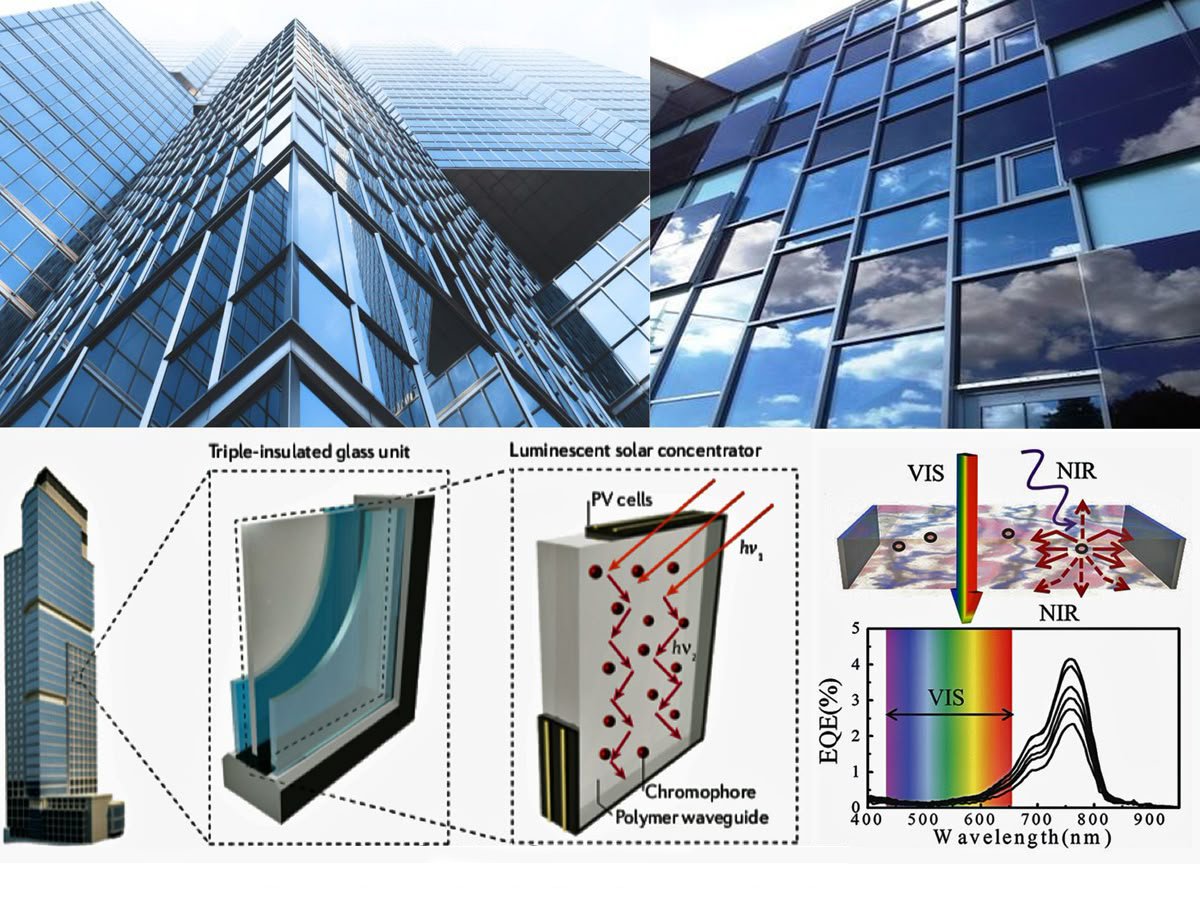

Photovoltaic glass operates by converting sunlight into electricity through embedded transparent solar cells. This technology is not only beneficial in reducing electricity consumption from non-renewable sources but also helps achieve zero-energy buildings, where the energy generated is equal to or greater than the energy consumed. Some PV glass panels are even equipped with color-tuning features, which allow them to adapt to changing sunlight conditions, improving efficiency and comfort within the building.
Another promising material in this category is solar-harvesting paint, which can capture solar energy and convert it into electricity. These paints are infused with light-absorbing nanomaterials, creating a whole new dimension of renewable energy in construction.
Advanced Insulation Materials: Aerogels and Phase-Change Materials
Insulation is one of the most critical aspects of sustainable construction, as it directly impacts a building’s energy consumption and thermal comfort. Traditional insulation materials like fiberglass and polystyrene are gradually being replaced by more advanced solutions such as aerogels and phase-change materials (PCMs).
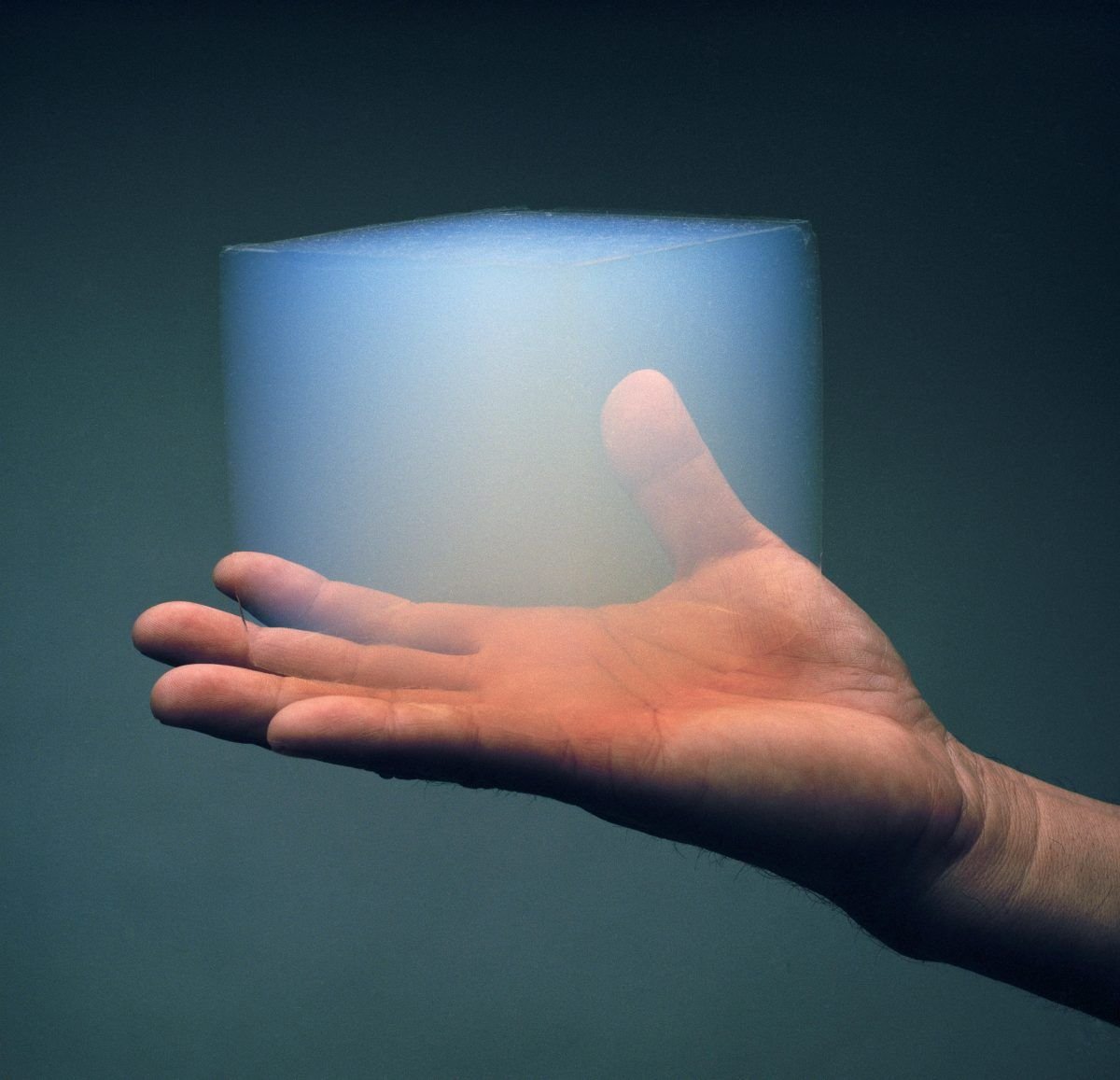
Aerogels, often referred to as frozen smoke due to their translucent appearance, are among the lightest and most effective insulating materials available. Despite being 90% air, aerogels provide exceptional thermal resistance, making them ideal for reducing heat transfer in buildings. Their superior insulation properties mean that thinner layers are required, optimizing space utilization in modern architecture.


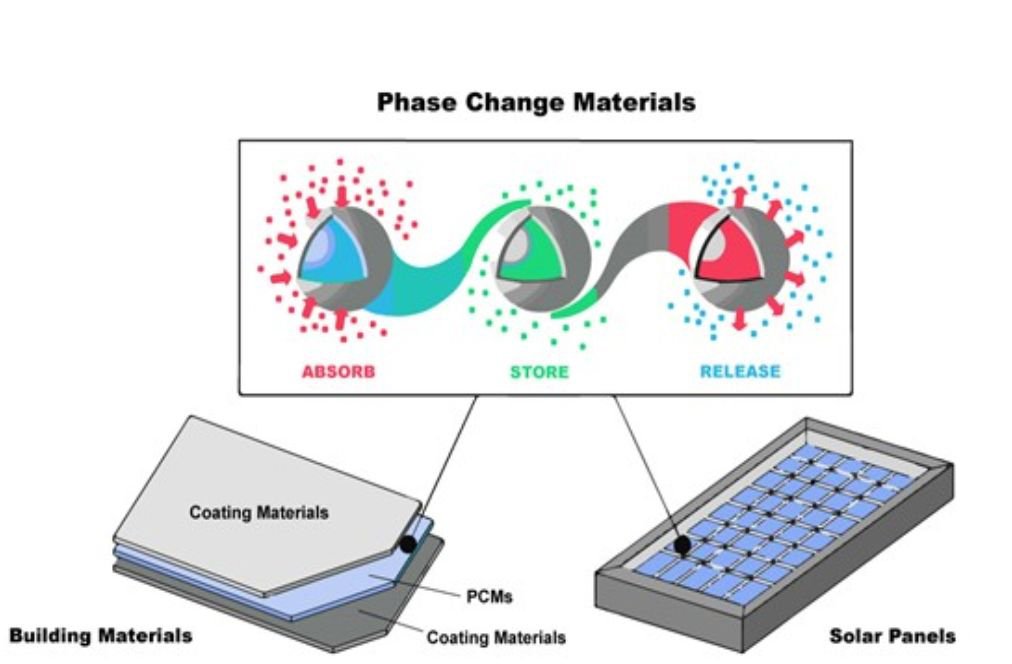
Another revolutionary insulation solution is phase-change materials (PCMs), which can absorb, store, and release heat depending on the surrounding temperature. PCMs undergo phase transitions, such as melting or solidifying, to regulate indoor temperatures passively. For example, in hot conditions, a PCM absorbs excess heat and melts, preventing overheating. At night, it releases the stored heat as it solidifies, maintaining a comfortable indoor climate. These materials significantly reduce the need for artificial heating and cooling, lowering energy consumption and operational costs.
Conclusion
Innovations in sustainable building materials are reshaping the construction industry by integrating smart technologies, renewable energy, and advanced insulation techniques. Self-healing concrete ensures longevity and reduces maintenance needs, while energy-generating materials like photovoltaic glass contribute to self-sufficient structures. Meanwhile, aerogels and phase-change materials are optimizing insulation, leading to better energy efficiency. As technology continues to advance, the role of these materials in reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability will become even more critical. Embracing these innovations is essential for building a future where architecture harmonizes with nature rather than exploiting it.
